Getting Started with Amazon Storage Service
Let’s learn something new everyday.
Getting Started with Amazon Storage Service
Today, I was looking for different blogs & articles regarding where to start my AWS journey. And I got various effective resources for learning & brushing up my AWS knowledge. And I have decided to share knowledge on linkedIn & twitter related to my learning path and the resource I am following.
Hey there , Congratulations, Since you are reading this , I assume that you also want to start learning.
As I am a big fan of reading documentations rather than video tutorials , I started my AWS journey by following “AWS skill builder”. Amazon Web Services Skill Builder, a web-based learning facility with numerous free cloud technology courses, now features paid subscription services.
Let’s start by enrolling in the AWS skill builder course “Storage Learning Plan: Object Storage”.
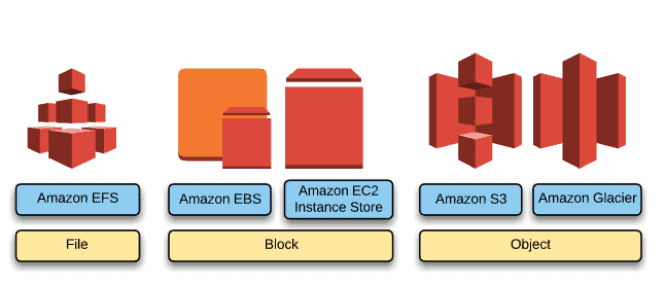
Primary storage types:
Let’s start from the core concept of storage. Whether on premises or in a cloud environment, there are three primary types of storage: block, file, and object.
Block storage:
Block storage is raw storage in which the hardware storage device or drive is a disk or volume that is formatted and attached to the compute system for use.
Example : Hard disk drives (HDDs), solid state drives (SSDs)
Amazon EBS is a good example of block storage.
Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) is an easy-to-use, scalable, high-performance block-storage service designed for Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2).
Use cases of block storage:
The storage device is used by the operating system or an application that has the capabilities to manage block storage directly Migrate mid-range, on-premises storage area network (SAN) workloads to the cloud. Deploying and scaling users choice of databases including the famous SAP HANA, Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, Cassandra, and MongoDB.
File storage
File storage is built on top of block storage, typically serving as a file share or file server.The two most common storage protocols for file storage are Server Message Block (SMB) and Network File System (NFS).The file system can be Windows Server, Linux, or a specialized operating system used on network attached storage (NAS) devices or clustered NAS systems.
AWS currently offers file storage using five different services.
- Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS).
- Amazon FSx for Lustre
- Amazon FSx for Windows File Server
- Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP
- Amazon FSx for OpenZFS.
Use cases of file storage:
File storage solutions are ideal for use cases such as large content repositories, development environments, media stores, or user home directories.
Object storage
Object storage solutions are ideal for building modern applications from the beginning that require scale and flexibility. The solution is also ideal for importing existing data stores for analytics, backup, or archive.
Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) is object storage in the AWS Cloud and Amazon S3 Glacier is used for archival storage at a lower cost per gigabyte (GB).AWS uses Amazon S3 as cost effective storage to store snapshots and backups of data stored in other core storage services such as Amazon EBS and Amazon EFS.
Use cases of AWS S3:
- Data lakes
- Websites
- Mobile applications
- Backup and restore
- Archive
- Enterprise
- applications
- IoT devices
- Big data analytics.
Got interesting to know about s3:
Amazon S3 is designed for 99.999999999 percent (11 9s) of durability. By default, you can create up to 100 buckets in each of your AWS accounts. The maximum file size that you can upload by using the Amazon S3 console is 160 GB
However I got Certificate of Completion of Storage of Amazon.
 I will continue my writting about AWS storage.
I will continue my writting about AWS storage.
Thank you very much for reading.